Improve Your Balance, Improve Your Brain Health

Balance Can Improve Your Brain Function
While phone apps and online programs that exercise the brain are popular to improve memory and prevent dementia, most people overlook a key component to lasting brain function--your balance. Your brain requires good balance to stay sharp and lower the risk of dementia. In addition to doing brain exercises, make sure you regularly challenge and improve your balance.
What does good balance have to do with preserving memory and brain function?
The cerebellum, the area at the base of the brain, governs balance as well as precision, coordination, and timing. It makes sure you can walk upright, put a spoon to your mouth, or hit a tennis ball. The movements of daily life keep the cerebellum in a constant state of activity. This constant activity keeps the rest of the brain on its toes.
A healthy cerebellum feeds the brain a steady stream of information to keep it actively firing and healthy. This is also one reason regular physical activity is so ...
ALS - A Complementary Approach with Supportive Supplements

Lou Gehrig's disease refers to a disorder called amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS. I don't frequently treat patients with ALS in my private practice, but I have encountered it enough times that I've done a good amount of research to discover how I can support my ASL patients. Some things I learned with my research:
- People with ALS have impaired methylation and high levels of oxidative stress and inflammation.
- Any effort to provide antioxidants, reduce sources of inflammation, and ensure proper methylation may assist in decreasing some of the mechanisms that are contributors to ALS.
- My treatment approach is a supportive, complementary approach. Not a cure or a replacement for standard medical care.
Many people with ALS have the genetic variants SOD and MTHFR. For some, these genetic variants make a big impact as the disease progresses. For others, these variants may make no impact at all. Below is additional information to help those looking for a way to further...
The Top 4 Common Reasons for Brain Fog
Do you space-out all the time? Does it feel as if you’re moving in slow motion through the fog and can’t snap out of it? Though it’s not considered a disorder worth a doctor’s visit, brain fog is nevertheless distressing, disorienting, and difficult to cope with. It’s also a red flag that your brain is aging too quickly and that you should take action right away.
Brain fog occurs when your neurons, or brain cells, don’t communicate well with one another. This poor communication causes overall brain function to slow down and diminish, giving you symptoms of brain fog.
The trick is to find out why those neurons aren’t communicating well with one another. There can be a number of reasons, both metabolic (having to do with diet and lifestyle) and neurological, that contribute to brain fog. In a nutshell, neurons need sufficient fuel, oxygen, and stimulation to function and prevent brain fog.
#1 Possible Cause: Blood Sugar is Too Low or Too High
Chronically unstable blood sugar is a ...
Conquer Your Allergies This Season

Dreading allergy season? The sun and wind arrive and suddenly it’s itchy skin, red eyes, a runny nose, sneezing, sinus pressure, and headaches. Likewise, you may react to certain foods with hives, headaches, nasal congestion, skin problems, a racing heart, or irritability.
What is the common denominator in both scenarios? Histamines. While many people just give up and suffer, some natural compounds can bring relief. To understand why these natural remedies work, it’s helpful to understand a bit about histamines.
What are Histamines?
Histamine is a protein that causes inflammation, redness, and irritation. It is produced in response to environmental or dietary proteins known as antigens. When the antigen comes in contact with the body, the immune system registers it as an intruder and produces antibodies to it. These antibodies cause a release of histamine into your bloodstream, and those histamines can build up with repeated exposure and increase your sensitivity.
Histamines are ...
Reverse Early Memory Loss with a Functional Medicine Approach

Reverse Early Memory Loss with a Functional Medicine Approach
Although genetics play a big role in who experiences memory loss with age, you don’t have to be a victim to the ravages of brain degeneration. By taking action at the early signs of memory loss, you can reverse your risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s before it’s too late.
One study showed that nine out of ten patients were able to reverse their memory loss when early intervention occurred. The same study subjects also showed significant long-term improvement in memory function. So what was the magic bullet? There was no magic. Just the solid implementation of functional neurology basics. Here’s what was done.
Study subjects underwent a dietary and lifestyle overhaul that included changes in what they ate, regular exercise, supplementation, better sleep, and exercising their brain. The improvements were so profound that some of the subjects were able to work again, having quit due to advancing memory loss.
Of the ten stu...
Must-Know Labs: Your Homocysteine Levels

Must-Know Labs: Your Homocysteine Levels
Once upon a time, Homocysteine was a lab value that was used to assess your risk of heart attack and stroke. It is not standard protocol to measure this anymore. As a matter a fact, nearly every patient or client I have worked with who has tried to get their primary care physician to run this number has been denied.
However, I couldn’t disagree more. Homocysteine is an important marker! Let’s explore some of the reasons why, as well as a few clinical observations I have made in regard to this value.
What is Homocysteine?
Homocysteine is an amino acid found in every cell of our body. Although the normal lab range for homocysteine is less than 10.4 umol/L, when placed on the finer-tuned ‘functional medicine scale,’ we prefer it to be nearer to 6-7 umol/L. That level is where it is both indicating optimal function and contributing to optimal function.
Homocysteine, when everything in the body is working as it should, is a precursor for some ...
How Food Sensitivities Develop

How Food Sensitivities Develop
All foods have proteins that are structured in a sequence. When you digest your food, your body’s enzymes break down those protein structures into chains of amino acids. If this break-down fails to happen, your immune system will see an unbroken protein sequence and says, “Hey! You don’t belong here, you’re foreign and it’s my job to attack and remove you.”
Your immune system then carries around the unbroken protein sequence and uses it as a flag to identify the food, preparing for the next time it sees the same protein sequence. If it sees the same protein sequence again, it will mount a faster immune response. This is the beginning of a food sensitivity. This is why it’s so important that our enzymes do a good job of breaking down protein sequences in the food we eat.
Food Coloring Prevents Protein Break-down
Food coloring can lead to food sensitivities. Artificial food coloring blocks the enzymes needed to break down protein structure seque
...Genetics and methylation – an introduction
You are the product of your genetics — if only it was so simple.
Every aspect of who you are, from the inside out and top to bottom, depends on your body’s ability to efficiently and correctly express your particular genetic makeup in the face of external factors. In many cases, even if you have genetic variations that lend a predisposition to illness, your choices may help limit, possibly reverse, negative genetic expressions through optimizing your diet and lifestyle.
We live in a fast-paced world filled with all kinds of products that, while they may help make our lives more efficient or pleasurable, may actually harm us in the long run. When you multiply certain genetic factors with lifestyle exposures, both acute and chronic illnesses may occur. Even those with optimal health and genetic expression may face health challenges due to external factors or poor personal choices. For example, genetically modified food, toxic chemicals, a leaky intestinal barrier (“leaky gut”), and syn...
A, D, E and K – Key Nutrients and Healthy Fat
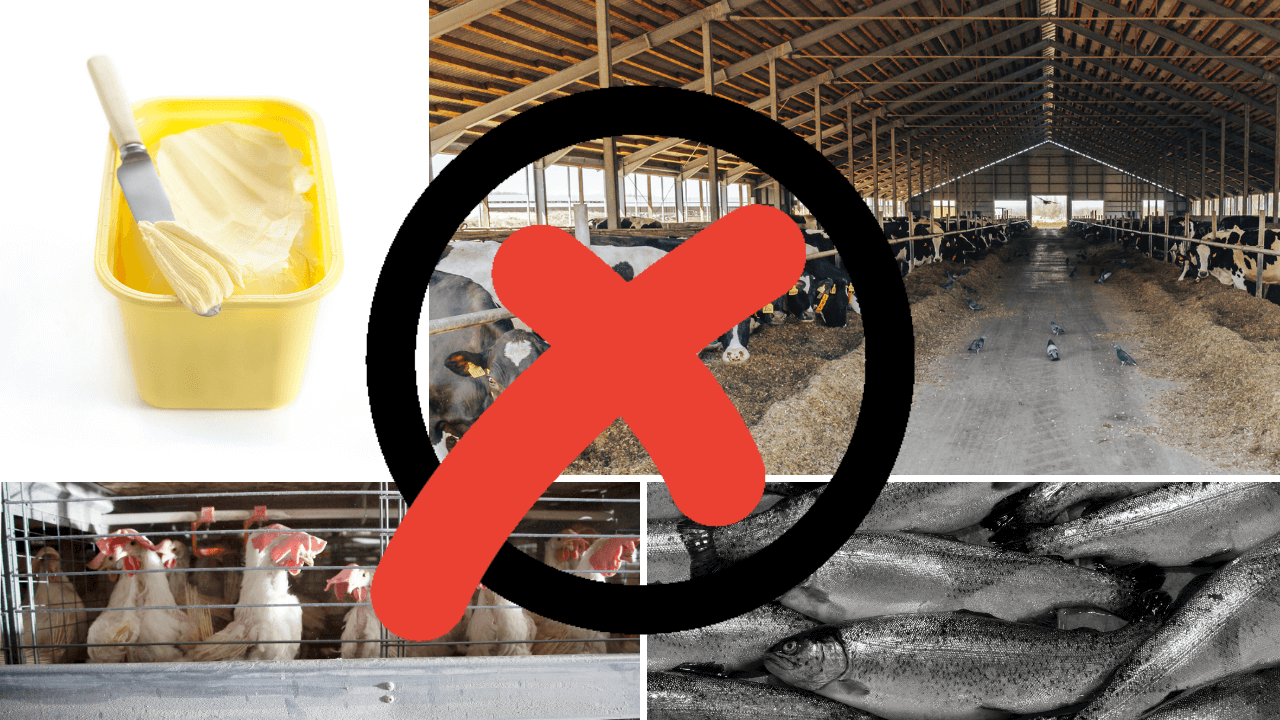

As you likely know, your body requires vitamins A, D, E, and K (potassium) among many other nutrients for optimum health. While these nutrients are easy to get naturally, they aren’t easily absorbed without being paired with fat. However, that doesn’t mean you should go out and pop your vitamins with a burger and fries.
When pairing nutrients with fat, it is important to opt for the healthiest forms of fats available. In addition to helping your body absorb these important vitamins, healthy fats also promote brain function, muscle building, and cellular repair. In fact, some studies even suggest that some good fats may help reduce symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease. That is exciting news, indeed!
The good fat and bad fat
Good fats help your body and overall health and bad fats do the opposite. The best sources of good fats are foods in their most natural state possible or from which oils have been extracted with minimal processing.
The good fats
Good fats help you to feel full and sa...
Fat is Your Friend

Name one of the most misunderstood nutrients in the American diet. Here’s a hint — it’s in the title of this post.
Fat has a reputation for being one of the worst things you could possibly eat. It’s been accused of causing obesity, elevated cholesterol and heart disease. However, we now know that fat can be good for you and is an important nutrient that should be part of your daily diet to maintain a healthy weight or manage chronic illness.
Fat, the misunderstood nutrient
Fat is just as important as protein, vitamins and minerals. For millennia, humans have consumed healthy fats in the form of natural plant oils from coconut, avocados, and olives and as natural components of wild game, wild-caught fish and grass-fed cows. Early people eating such traditional, natural diets typically had far fewer chronic health conditions and live longer when compared to peers eating processed foods, farmed fish, or feed-lot beef.
With the rise of mass manufacturing and the ability to process ...

